plusieurs approches sont possible
1 . Non YAML write /S2I
prerequis : activer le plugin xpaas pour bénéficier de image openjdk8 embeeded par RHEL
autre posssibilité oc import-image <image>
$ minishift addons apply admin-user
$ oc login -u system:admin
$ oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-admin admin
$ oc login -u admin -p admin
$ minishift addons apply xpaas
exemple de source https://github.com/piomin/sample-spring-microservices-new
La vue dans onglet Build

$ oc new-app redhat-openjdk18-openshift:1.3~https://github.com/piomin/sample-spring-microservices-new.git#openshift --name=employee --context-dir=employee-servicoc new-project tutorial$ oc new-app redhat-openjdk18-openshift:1.3~https://github.com/piomin/sample-spring-microservices-new.git#openshift --name=department --context-dir=department-service -e EMPLOYEE_SERVICE=employee
//injection des variables environnements to BuildConfig object
$oc set env bc/employee --from="secret/mongodb" --prefix=MONGO_
OpenShift crée par défault pour chaque nouvelle appliction les éléments suivants
- BuildConfig
- DeploymentConfig
- Service
- ImageStream
build le tout avec maven puis le sauvegarde dans la registry Docker
- Manual Build
oc start-build department
- Get all the build
oc get bc
- get Runing pods
oc get pods -w


- Repository Image Build > images

- Exposition des routes
oc expose svc istio-ingressgateway –port=80
oc expose svc grafana
oc expose svc prometheus
oc expose svc tracing
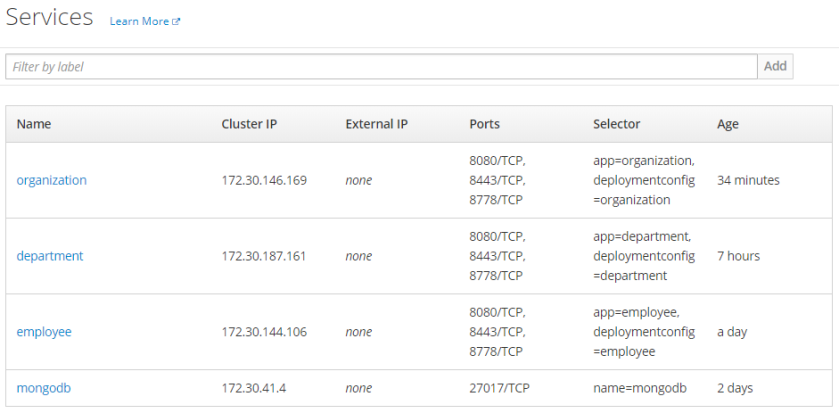
TEST application
After that, we can access applications atthe address http://${APP_NAME}-${PROJ_NAME}.${MINISHIFT_IP}.nip.io, as shown below.
$ oc expose svc employee $ oc expose svc department $ oc expose svc organization
After that, we can access applications atthe address http://${APP_NAME}-${PROJ_NAME}.${MINISHIFT_IP}.nip.io, as shown below.

2 Deploy with YAML
Preparing OpenShift deployment descriptor
When working with OpenShift, the first step of application’s deployment is to create YAML configuration file. This file contains basic information about deployment like containers used for running applications (1), scaling (2), triggers that drive automated deployments in response to events (3) or a strategy of deploying your pods on the platform (4).
kind: "DeploymentConfig"
apiVersion: "v1"
metadata:
name: "account-service"
spec:
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: "account-service"
spec:
containers: # (1)
- name: "account-vertx-service"
image: "piomin/account-vertx-service:latest"
ports:
- containerPort: 8095
protocol: "TCP"
replicas: 1 # (2)
triggers: # (3)
- type: "ConfigChange"
- type: "ImageChange"
imageChangeParams:
automatic: true
containerNames:
- "account-vertx-service"
from:
kind: "ImageStreamTag"
name: "account-vertx-service:latest"
strategy: # (4)
type: "Rolling"
paused: false
revisionHistoryLimit: 2
|
Deployment configurations can be managed with the oc command like any other resource. You can create new configuration or update the existing one by using oc apply command.
|
1
|
$ oc apply -f account-deployment.yaml oc set env --from=secrets/mongodb dc/account-service |
Image DOCKER change YAML (trigger) oc apply -f account-image.yaml
apiVersion: "v1" kind: "ImageStream" metadata: name: "account-vertx-service" spec: dockerImageRepository: "piomin/account-vertx-service"
running the deployment
oc rollout latest dc/account-service
oc rollout latest dc/customer-serviceRun a new Docker image in Openshift
oc new-app --docker-image=myfear/swarm-sample:latest
oc describe service swarm-sample
- oc import-image my-redhat-openjdk-18/openjdk18-openshift --from=registry.access.redhat.com/redhat-openjdk-18/openjdk18-openshift --confirm
install Openfaas stack
install docker machines for windows
$ base=https://github.com/docker/machine/releases/download/v0.16.0 && mkdir -p "$HOME/bin" && curl -L $base/docker-machine-Windows-x86_64.exe > "$HOME/bin/docker-machine.exe" && chmod +x "$HOME/bin/docker-machine.exe" ***** add docker machines in the PATH system
docker-machine create -d virtualbox --virtualbox-cpu-count "2" --virtualbox-memory "2048" --virtualbox-disk-size "25000" tutorieldocker-machine env tutorieldocker-machine start tutoriel
* log to docker machine with ssh docker-machine ssh tutoriel
**** install faas cli git clone https://github.com/openfaas/faas.gitcurl -sSL https://cli.openfaas.com | sudo sh
document annexe https://github.com/openfaas/faas-cli
****************************************installation Open faas sur minishift https://blog.openshift.com/openfaas-on-openshift/
$ git clone https://github.com/mhausenblas/faas-netes.git$ cd faas-netes/$ git checkout openshift
install oc client https://docs.okd.io/latest/cli_reference/get_started_cli.html#cli-windowsdownload the client https://github.com/openshift/origin/releases
oc new-project openfaas-fnoc new-project openfaasoc create sa faas-controlleroc policy add-role-to-user admin system:serviceaccount:openfaas:faas-controller --namespace=openfaas-fn role "admin" added: "system:serviceaccount:openfaas:faas-controller"cd yamloc apply -f alertmanager_config.yml,alertmanager.yml,faasnetesd.yml,gateway.yml,nats.yml,prometheus_config.yml,prometheus.yml,queueworker.ymloc expose service/gateway https://developer.jboss.org/en/jberet/blog/2018/09/17/build-and-deploy-containerized-java-batch-applications-on-openshift?_sscc=t
| https://medium.com/@pablo127/deploy-spring-boot-application-to-openshift-3-next-gen-2b311f55f0c5 |


![WorldCat lets people access the collections of libraries worldwide [WorldCat.org] WorldCat lets people access the collections of libraries worldwide [WorldCat.org]](http://www.worldcat.org/images/wc_badge_120x60.gif?ai=sungard_myartaud)